•Script Commands are GUI-oriented in regards to VERTEX's structure and workflow.
•You can trigger simple actions, switch settings, or operate with values.
•Get to know the basic structure & syntax and familiarize yourself with some simple script examples.
•To learn how to create a script go to the topic Scripts.
Simple Actions
Enter short and simple commands into a scripting field or into the command line and trigger an action.
Playback1.Play
Playback2.Stop
Playback3.GotoCue 1
GUI-Oriented Structure
Script Commands are tailored to resemble working with VERTEX's graphical user interface.
The syntax and structure should look very familiar to you if you already know how to work with the GUI.
Almost every property in VERTEX can be scripted.
Example: Set Opacity of ClipContainer1 in Playback1 to a Value
Follow the numbered markers in the screenshots to understand the order in which script commands are composed and what structure in the GUI they represent.
For example: In Sequence1, ClipContainer1 set opacity value to 0.5:
+
+
Script Command:
Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value = 0.5
Set System 1 to Fullscreen
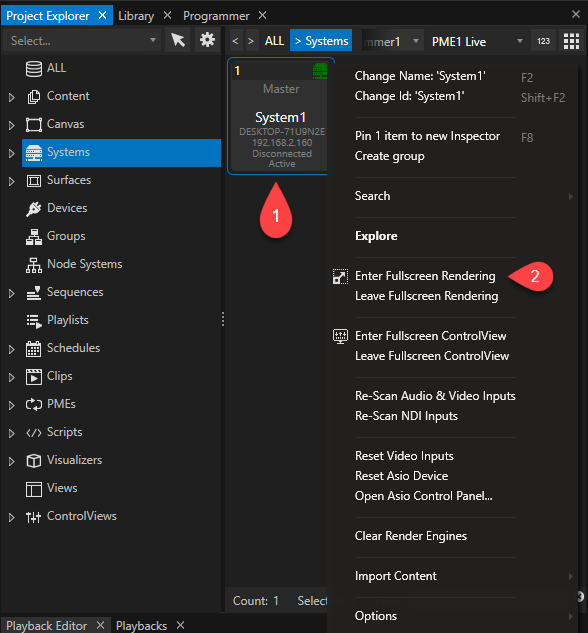
Set System 1 to Fullscreen
+
Script Command:
System1.EnterFullScreen
Disable Preview in Fullscreen for System1
Disable Preview in Fullscreen for System1
+
+
Script Command:
System1.Settings.DisablePreviewInFullscreen.Value = true
Autocomplete ScriptWizard
In every scripting field VERTEX's ScriptWizard will provide you with a list of all available items, commands and actions.
Use the shortcut "CTRL+ Space" in an empty line to open a full list of all available elements.
Enter a decimal point to open a list of all available child options and elements.
For every list item the expected parameters are shown.
Confirm your choice with ENTER for the created script to take effect.
Structure and Syntax
 The availability of script commands and syntax options depends on your current VERTEX version.
The availability of script commands and syntax options depends on your current VERTEX version.
With every version, we improve and extend the software feature set - including script commands.
Not all script commands or options like local variables or script tags are supported by older versions.
Basic structure
The next deeper level is initiated by a decimal point.
Firstlevel.Secondlevel.Thirdlevel.
One script command per line, use a new line for the next script command .
Playback1.Play
System1.Settings.DisablePreviewInFullscreen.Value = false
Comments are preceded by a double slash.
//This is a comment
Value Operations
Value
Set or read a value:
Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value = 0
Set properties with multiple values in one line:
Canvas2.Size 1920, 1080
FadeValue
Fade to a new value in a defined time- first parameter is value, second parameter is time in seconds.
Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.FadeValue 1,2
ProgValue
Read or create a value in programmer mode:
Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.ProgValue = 0
FadeProgValue
Sets a new value in programmer and fades to this value - first parameter is value, second parameter is time in seconds.
Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.FadeProgValue 1,2
Assign Values
Use an equal sign for the following value operations:
Value
Value = 1
Value = 2000
Value = 0.5
Value = 0,1,0.1 // <-- for e.g. DMX Values that consist of r,g,b
Colors
//RGB
Value = #123 111 100
//ARGB
Value = #50 100 100 100
//RGB as Hex
Value = #FFFFFF
//ARGB as Hex
Value = #30FF00FF
//normalized RGB
Value = 0.5,0.5,0.5
//normalized ARGB
Value = 0.5,1,1,1
//normalized RGB
Value = {R:1.0,G:0.1,B:0.5}
//normalized ARGB
Value = {A:0.5,R:1.0,G:0.1,B:0.5}
Value = {R:10,G:100,B:50}
Value = {A:255,R:10,G:100,B:50}
Checkboxes
true and false
Value = true
Value = false
Settings
Use the name that is used in inspector dropdowns and property fields.
Value = FreeSync
Value = System2
Allocate Text or URLs
Value = Hello World
Value = www.ioversal.com
Return A Current Value
Value (without equals)
Entering Value (or ProgValue) returns the current value of an item.
Playback1.Clipcontainer1.Opacity.Value
•the return value is e.g 0.5 when clip container's opacity currently is 0.5
•use return values also for an external request over the API
Return A Value From An Item & Assign To Another Item
You can combine both variants - assign and return - to read out one item's value and assign it to another item.
Set notes from Clip Container 1 as Text into Text Content2
Content2.Settings.Text.Value = playback1.ClipContainer1.UserProperties.Notes.Value
Trigger Actions
- for example in a system:
System2.ControlViewer.Open
System1.WindowsShutdown
Local Variables
When setting a local variable, there must be a single value (not a formula like the syntax for "Eval") on the right side of the equation.
Set cnt = 1
Set cnt = Thisisatext
Assigning a value from a property to your local variable.
Set cnt = Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value
Eval
Defines, evaluates or updates a local variable, property or method. The right side of the equation is evaluated as a formula (called "expression").
Eval cnt = cnt + 1
Assign values of other variables.
Set max = 100
Eval cont = cnt <= max
Assign values to properties or methods: The evaluated expression is assigned to the property on the left side of the equation - or passed as a parameter to a method.
Eval Surface2.CanvasOffset.X = [Surface1.CanvasOffset.X] + 1920
Eval Sequence1.ClipContainer2.Opacity = [Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity] * 2
Nested elements require square brackets (unlike the syntax for Set).
Specify strings with single quotes.
Eval cnt = 'CNT: ' + Round([Playback1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value], 2)
// the variable cnt gets the (new) value based on a string and the rounded
// opacity value from ClipContainer1
The script command Eval also returns the assigned value, which allows complex programming in e.g. C#:
//This assignes a new value to Sequence1.ClipContainer2.Opacity and returns this value to Script.Run in C# and its variable 'opacity'.
var opacity = Script.Run<int>("Eval Sequence1.ClipContainer2.Opacity = [Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity] * 2");

Rule of thumb:
Whenever a parameter needs to be assessed, start the line with Eval. This parses the whole parameter (everything on the right side of the equation) as an expression.
Expression-/Eval-Commands
These self-explainatory commands can also be found in the Expressions-Node:
ToInt
ToDouble
ToString
ToFloat
ToByte
ToBool
Local variables can use the same methods as the Variable core objects (if applicable):
ReadSplitString ParseJsonMember CreateJson AddRawText AppendRawText AddText CombineText AppendText AddAsText CombineAsText AppendAsText FormatNumber GetSplitString GetContainsString GetSubString GetSubStringRegion GetReplaceString GetTextLine GetFileTimeName AddNumber SubtractNumber MultiplyNumber DivideNumber |
FloorNumber CeilingNumber RoundNumber AbsNumber MinNumber MaxNumber RangeNumber GetRangeNumber HttpRawRequestDownloadToDisc HttpRequestDownloadToDisc ExecuteAsObjectScript ExecuteAsScript HttpPostRequest HttpPostRequestAuth HttpPut HttpPost HttpDelete SetRawValue Clear AddLine AddEmptyLine IsNullOrEmpty |
Conditions
In the fashion of easy script commands, we have implemented simple conditional operations.
IfEqual
Executes a specified script if parameter a = b. Parameters: a, b, Script
IfEqual Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value, 0, Script2
IfExecute
Executes a specified script if the specified expression is true.
IfExecute myval, Script1
IfGreater
Executes a specified script if parameter a > b. Parameters: a, b, Script
IfGreater Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value, 0, Script2
IfLesser
Executes a specified script if parameter a < b. Parameters: a, b, Script
IfLesser Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value, 1, Script2
IfUnequal
Executes a specified script if parameter a is not b. Parameters: a, b, Script
IfUnequal Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value, 0, Script2
Tags
Defining and jumping to tags in a script:
:Tag
Identifies and tags a line in a script. By using the Goto Tag command, script execution will be able to jump between tagged lines instead of going through the script lines top to bottom.
:start
:part3
:marker2
The tag name is preceded by a colon without a space. Tags must be placed at the beginning of the line that is supposed to be tagged. Examples can be found here.
Goto Tag
Jumps to the tagged line inside a script - in the actual script command, the tag name must be specified without a colon.
Goto part3
IfGoto variable, tag
Continues to a specified tag if the specified expression is true.
Set Variable1= true
IfGoto Variable1, start
Special Commands
Wait
Wait´## seconds
Wait 10
WaitAll
Wait for all executing child scripts to finish.
WaitAll 10
Cancel
Cancels all running scripts.
Cancel
log
logs the returned value - the result is shown in script monitor's console and notification window
use for e.g testing commands, preparing commands for the API...
log Playback1.Clipcontainer1.Opacity.Value
log a text
log thisisatext
log this is a text
logs a local variable or script parameter
Set variable1=50
log variable1
Call renamed items
An item can be called from a script by either its type-ID or its name. Both will be accepted.
Example:
Device1 ( a 8 Bit Dimmer) was renamed to "Dimmer1"
The device can be called by both names:
Dimmer1.Settings.StartAddress.Value = 3
Device1.Settings.StartAddress.Value = 3
Indexers
In the context of Vertex scripts, indexers refer to a syntax that allows accessing several items at once, e.g.:
Playback[1-2].Play
Internally this is resolved to several script lines:
Playback1.Play
Playback2.Play
This feature can be used as a powerful way to remote control multiple items with the touch of one button, for instance if indexers were used in a Control View script for a button/ slider etc..
Several Indexers can be used together, e.g.:
Sequence[1-2].ClipContainer[1-2].Opacity.Value = 1
This will be resolved to:
Sequence1.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value = 1
Sequence2.ClipContainer1.Opacity.Value = 1
Sequence1.ClipContainer2.Opacity.Value = 1
Sequence2.ClipContainer2.Opacity.Value = 1
Indexers can be used to access any scriptable objects. Even if a custom name is not specified, the objects are always accessible by their generic script name appended by their Script Id.
The indexer expression is enclosed in "[ ]" brackets and appended to the common or generic script name, as in the examples above.
An indexer expression can consist of several filter expressions, each separated by one or more spaces.
A filter expression can represent either a single value or a value range. To specify a range, concatenate the two values using "-" as seen in the examples above.

Important: do not add any spaces between the two range values!
Valid values are either integers for filtering by Id or time codes for filtering Clip Containers by their playback position.
Value ranges must be of the same type, i.e., combining Id and time filters is not possible.
If the entire indexer expression or a value expression is a valid token expression (e.g. "Variable1.Value"), it will be evaluated before being further examined.
Tokens that can be used in this context are:
•Any properties that return a value that can be evaluated here e.g.: 1, "1-2", "3:00:00“.
•A Playback for filtering items using the current playback time.
•A Sequence Cue for filtering items using the cue’s position.
 Note: Local variables and parameters cannot be used, because the Indexers are evaluated before actually executing the script, using a common, global scope.
Note: Local variables and parameters cannot be used, because the Indexers are evaluated before actually executing the script, using a common, global scope.
Each filter expression can optionally start with a prefix that acts as a „modifier“ and impacts how the expression is evaluated:
Modifier |
Effect |
Comments |
- |
Exclude value or range |
Legacy syntax, identical to "!" |
! |
Exclude value or range |
|
+ |
Include value or range |
Legacy syntax, obsolete |
> |
Include values greater than (or equal to)… |
Not for ranges |
< |
Include values lesser than (or equal to)… |
Not for ranges |
* |
Include selected items |
When using several filter expressions, an object is accepted if it matches at least one inclusive filter and not any exclusive filters.
Empty Indexer expressions will include all members (with the specified generic script name).
Invalid Indexer expressions will prevent the entire script from executing and throw an exception.
Valid Indexer expressions that yield no results during execution will be logged as a warning.
Notes regarding Clip Container filtering by time:
•Single time values will match if the time is within the Clip Container’s range.
•“Greater than” filters will match if the Clip Container starts after the specified time.
•“Lesser than” filters will match if the Clip Container ends before the specified tine.
•A specified time range will match if it overlaps with the Clip Container in any way.
Examples
Sequence1.ClipContainer[].Opacity.Value=1
Sequence1.ClipContainer[1-5].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[7 9].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[<5].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[1-2 9-10 4-7 -5-6].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[5:0:0].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[-Sequence1.Cue2].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[Sequence1.Cue2].Opacity.Value=0.2
Sequence1.ClipContainer[>Playback1].Opacity.Value=0.2
Setting new opacity value on selected items:
Sequence1.ClipContainer[*].Opacity.Value=0.1
Setting new opacity value on all clip containers on a specified track.
Sequence1.ClipContainer[Sequence1.Tracks.Track2].Opacity.Value=0.1
Changing size value of all click buttons on a specified ControlView page.
ControlView1.Controls.ClickButton[ControlView1.Pages.Page1].Settings.Size.Width.Value = 200
Changing size value of all click buttons on ControlView page1 and higher.
ControlView1.Controls.ClickButton[>ControlView1.Pages.Page1].Settings.Size.Width.Value = 200
Changing size value of all click buttons on ControlView page1 and page2. Pages listing separated by space.
ControlView1.Controls.ClickButton[ControlView1.Pages.Page1 ControlView1.Pages.Page2].Settings.Size.Width.Value = 200 è auf Page1,Page2; Page-Auflistung mit Space getrennt


